Node.js File System Module
Learning how to work with file system of computer
Generally, we use Graphical User Interface (GUI) to work with file system of our computer. Developers also use Command Line Interface (CLI) to work with file system of computer. But what if we want to work with file system of our computer through JavaScript code ?
Node.js has one built-in module i.e. Node.js File System Module. This module allows us to work with file system of our computer.
With the help of this module, we can
a) make a new directory
b) remove any existing directory
c) create a new file & write data into it
d) append data into a file
e) read data from a file
f) copy data from one file to another file
g) delete a file
Enough talk. Let's go for action. Let's create a file named script.js Since Node.js File System Module is a built-in module so we don't need to install it into our computer. Only thing we have to do is to incorporate this module into our script.js file such as
const fs = require('fs');
Let's perform all the above operations one by one.
a) To make a new directory with "mydir" name, write the following code
fs.mkdirSync("mydir")
Now run this script by executing following command in the terminal
$ node script.js
b) To remove an existing directory with "mydir" name, write the following code
fs.rmdirSync("mydir")
Now run this script by executing following command in the terminal
$ node script.js
c) To create a file with "text1.txt" name & write "Hello world" into it, write the following code
fs.writeFileSync("text1.txt", "Hello world")
Now run this script by executing following command in the terminal
$ node script.js
This will create a new file with following output
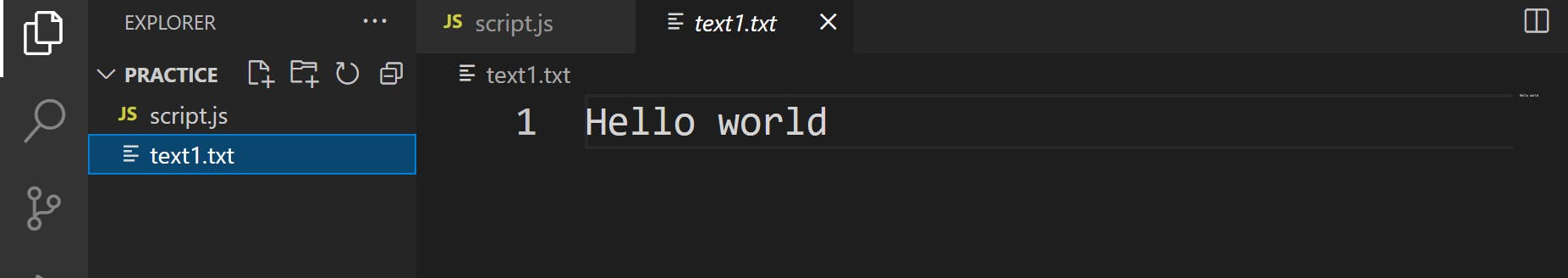
d) To append "Hello developers" into this file, write the following code
fs.appendFileSync("text1.txt", "Hello developers")
Now run this script by executing following command in the terminal
$ node script.js
This will append data to end of file
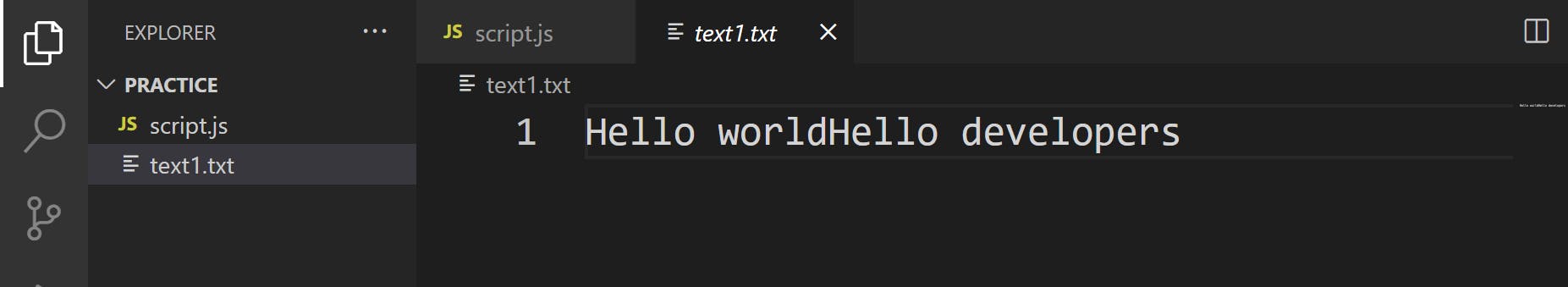
e) To read data from file, write the following code
const buffer = fs.readFileSync("text1.txt")
Since this data is in buffer form, we have to convert it into string form. To do so, write the following code
const data = buffer.toString()
let's log this data into console
console.log(data)
Now run this script by executing following command in the terminal
$ node script.js
read data in the console
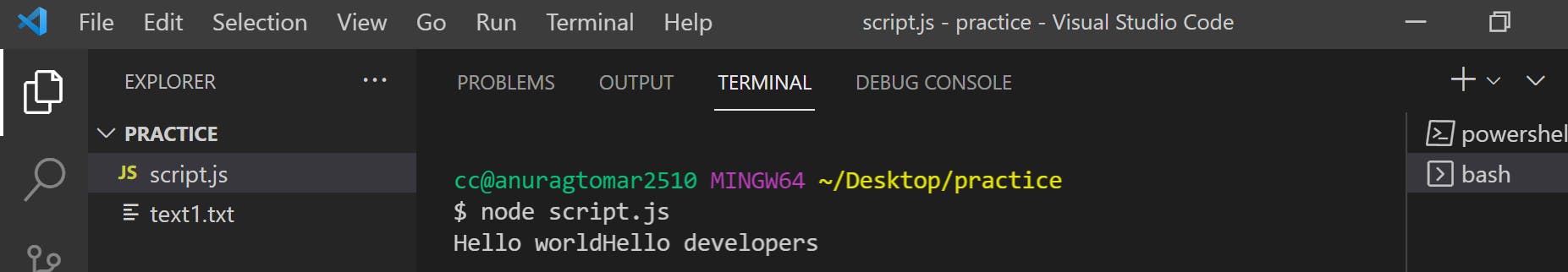
f) To copy data from "text1.txt" to a new file with name "text2.txt", write the following code
fs.copyFileSync("text1.txt", "text2.txt")
Now run this script by executing following command in the terminal
$ node script.js
Copied data in "text2.txt" file
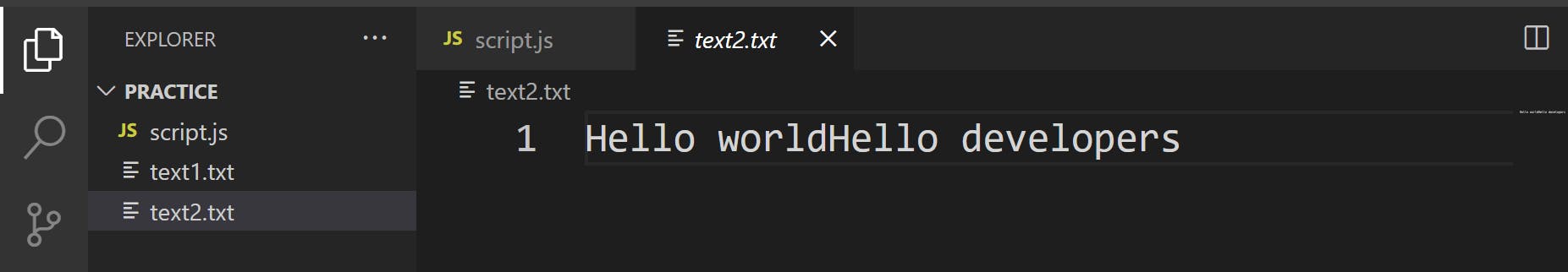
f) To delete an existing file with "text1.txt" name, write the following code
fs.unlinkSync("text1.txt")
Now run this script by executing following command in the terminal
$ node script.js
That's all. Happy learning!
